Is BMI the Key Factor in Deciding Bariatric Surgery Candidacy?
Why do we need to take a step toward bariatric surgery?
The primary purpose of bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustained weight loss. The surgical procedures aim to reduce the stomach size or alter the digestive system to restrict food intake and promote weight loss. So, for a better quality of life and to defeat obesity, you must step towards bariatric surgery.
The primary objectives of bariatric surgery are:
· Weight Reduction
Bariatric surgery is the best way to facilitate substantial weight loss in individuals with severe obesity. These surgical procedures help limit the amount of food a person can eat and absorb. And these procedures do so by restricting the capacity of the stomach to hold food or by rerouting the digestive system. As a result, patients typically experience significant weight loss over time. So, weight loss surgery is an effective solution to obesity.
· Improvement of Obesity-Related Health Conditions
Bariatric surgery can lead to improvements or even the resolution of several obesity-related health conditions. Conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, joint pain, and heart disease are commonly associated with obesity. By achieving substantial weight loss, many patients experience positive changes in these health conditions, which improve their health and reduce the risk of related complications. Therefore, weight loss surgery helps to treat heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other obesity-related complications.
· Enhancement of Quality of Life
Severe obesity can profoundly impact an individual’s quality of life. Physical limitations, reduced mobility, social stigma, and psychological distress are common challenges faced by individuals struggling with obesity. Bariatric surgery can help improve physical mobility, alleviate joint pain, enhance self-esteem, and boost overall well-being. That is why for leading to an improved quality of life, obese patients should take a step toward bariatric surgery.
How to know if you are the best candidate for bariatric surgery?
Determining if you are the best candidate for bariatric surgery requires a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. While each individual’s situation is unique, several key factors must be considered when assessing your candidacy for bariatric surgery.
Here are some indicators that may suggest you are a suitable candidate:
· BMI and Weight Status
Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for individuals with a BMI of 40 or above (Class III obesity) or a BMI of 35 or higher (Class II obesity) with significant obesity-related comorbidities. If your BMI falls within these ranges, it may indicate that you are a potential candidate for weight loss surgery.
· Obesity-related Comorbidities
Bariatric surgery is often best for individuals with health issues related to obesity, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, or cardiovascular disease. If these comorbidities impact your overall health and quality of life, bariatric surgery may be an appropriate option.
· Failed Attempts at Non-surgical Weight Loss
Weight loss surgery is typically recommended for individuals who have substantially tried to lose weight through non-surgical methods but have not achieved significant and sustained results. If you have tried various weight loss interventions, including lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and exercise, without success, take a step towards bariatric surgery to achieve significant weight loss.
· Commitment to Lifestyle Changes
Bariatric surgery is a challenging fix. It requires a lifelong commitment to significant lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications, regular exercise, and adherence to post-operative guidelines. If you are willing to make and sustain these lifestyle changes to support your weight loss and overall health, you may be a good candidate for bariatric surgery.
· Psychological Evaluation
Obesity often has psychological components, and bariatric surgery can impact mental health. A thorough psychological evaluation is typically conducted to assess your emotional and behavioral readiness for the surgery and its associated lifestyle changes. You may be a suitable candidate if you are psychologically prepared and have a support system. Therefore, take a step towards bariatric surgery and change your life.
Body Mass Index an initial assessment and a Step towards bariatric Surgery
Body Mass Index (BMI) is an initial assessment tool for determining the suitability of weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery. It provides healthcare professionals with a quantitative measure that relates an individual’s weight to height, indicating their overall weight status.
BMI Calculation and Categories
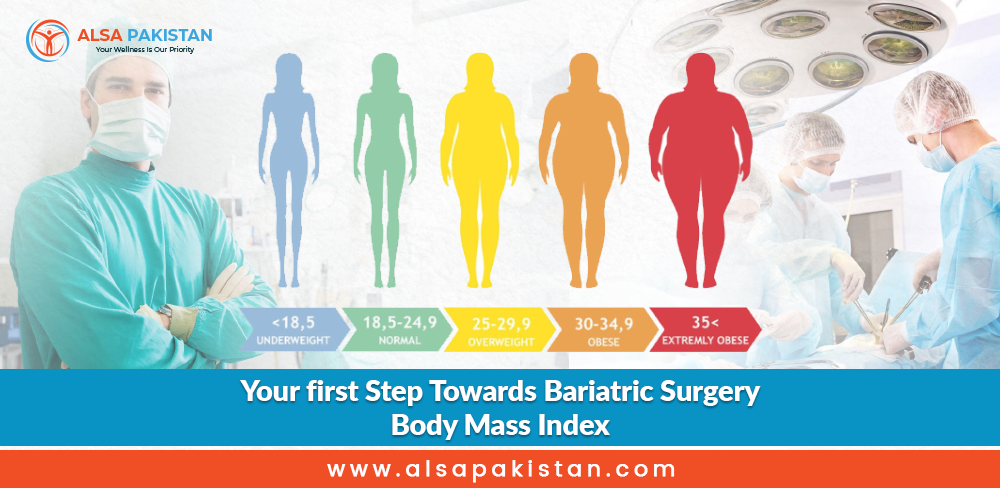
The BMI calculator divides your weight(kilograms) by the square of your height(meters), that is (BMI = weight in kg / (height in meters)^2). The resulting value is then categorized into different weight status categories:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obesity:
- Class I: BMI between 30 and 34.9
- Class II: BMI between 35 and 39.9
- Class III (Morbid Obesity): BMI 40 or higher
BMI Calculator as an Initial Assessment Tool
BMI serves as an essential initial assessment tool for weight loss surgery due to several reasons:
- Screening Eligibility
Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for individuals with severe obesity. BMI helps healthcare professionals identify individuals with a BMI in Class II (35 or higher) or Class III (40 or higher) obesity category who may be suitable candidates for weight loss surgery.
- Objective Measurement
BMI provides an objective measurement that is easy to calculate and widely recognized in the medical field. It helps standardize the assessment process and allows for consistent evaluation across healthcare providers.
- The Severity of Obesity
BMI helps determine the severity of obesity by quantifying the excess weight to height. Individuals with higher BMI values often have a greater excess weight, which may indicate a higher likelihood of obesity-related health complications. And BMI value is also a first step towards bariatric surgery which gives you a life-changing experience.
- Predicting Surgical Outcomes
Research has shown that individuals with higher BMIs often experience more significant weight loss after bariatric surgery. BMI calculation helps predict the expected weight loss outcomes and assists in setting realistic goals for patients considering weight loss surgery.
- Comorbidity Evaluation
BMI is closely associated with obesity-related comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. Individuals with higher values of BMI are more likely to have these comorbidities, and weight loss surgery can significantly improve or even resolve them. BMI assessment aids in evaluating the impact of obesity on overall health and the potential benefits of surgical intervention.
Bariatric Surgeries: An effective treatment of Obesity
Bariatric surgery, or weight loss surgery, is emerging as a powerful tool in the battle against obesity. With the increasing prevalence of obesity worldwide, bariatric surgeries offer a potential solution for individuals struggling with significant weight-related health issues. Let us comprehensively analyze bariatric surgeries, including their types, benefits, risks, and considerations for potential candidates.
Types of Bariatric Surgeries
There are several types of bariatric surgeries, each with its unique mechanism and impact on weight loss. The commonly performed procedures include:
· Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB)
In Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, surgeons create a small pouch at the top of the stomach. After that, they connect this pouch to the small intestine. This restricts the amount of food intake and reduces nutrient absorption.
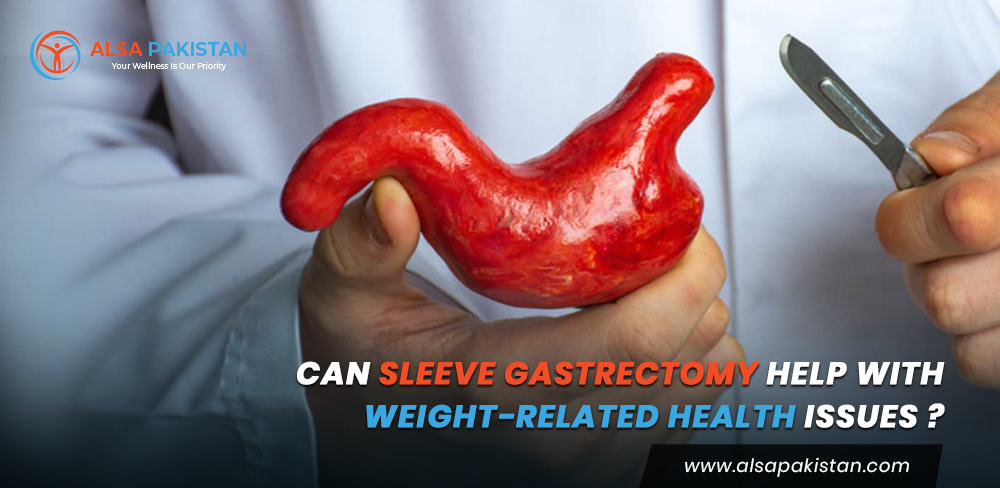
· Sleeve gastrectomy
In this type of weight loss surgery, surgeons remove a large part of the stomach, leaving behind a small, banana-shaped sleeve. In sleeve gastrectomy, the reduced stomach size restricts food intake and results in early satiety.
· Duodenal Switch
A duodenal switch combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a bypass of a significant portion of the small intestine. This surgical procedure involves removing a part of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to reduce the absorption of calories and nutrients. The duodenal switch offers a high degree of malabsorption and can lead to significant weight loss but may also have more nutritional considerations.
· Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
BPD/DS is a complex procedure involving restrictive and malabsorptive components. It combines a sleeve gastrectomy with a bypass of a large portion of the small intestine. BPD/DS results in significant weight loss but requires lifelong nutritional supplementation due to the higher risk of dietary deficiencies.
· SADI (Single Anastomosis Duodeno-Ileal) bypass surgery
The SADI (Single Anastomosis Duodeno-Ileal) bypass surgery, also known as loop duodenal switch or single-anastomosis duodenal switch, is a relatively newer weight loss surgical procedure. It is a modification of the traditional duodenal switch surgery and combines aspects of sleeve gastrectomy and intestinal bypass.
The SADI bypass surgery offers both restrictive and malabsorptive components. The reduced stomach size limits food intake, while the bypassed portion of the small intestine decreases nutrient absorption, leading to weight loss. The SADI bypass aims to achieve significant and sustained weight loss by combining these mechanisms.
Benefits of Bariatric Surgeries
Bariatric surgeries offer numerous benefits beyond weight loss, improving physical and psychological well-being. Some key benefits include:
· Sustainable Weight Loss
Bariatric surgeries typically result in significant and sustained weight loss. This weight reduction alleviates obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
· A step toward surgery gives a better Life
Bariatric surgery often leads to enhanced mobility, increased self-esteem, and improved overall quality of life. Patients report reduced joint pain, improved physical activity, and increased social participation.
· Resolution of Metabolic Disorders
Many obesity-related metabolic disorders, such as type 2 diabetes, have been shown to improve or even resolve after bariatric surgery. This can result in reduced medication dependence and improved glycemic control.
Get rid of obesity and take a step towards weight loss surgery
Therefore, the primary purpose of bariatric surgery is to provide individuals with severe obesity a tool to achieve substantial weight loss, improve obesity-related health conditions, and enhance their overall quality of life. So, take a step towards bariatric surgery.
But It is important to note that bariatric surgery is not a stand-alone solution for weight loss. It is typically part of a comprehensive treatment approach that includes pre-surgical evaluation, cost of bariatric surgeries in Pakistan, post-operative care, and long-term lifestyle changes. These changes often involve adopting a healthier diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and addressing psychological and emotional aspects of weight management.
Finally, bariatric surgery should be approached as a collaborative effort between patients, healthcare professionals, and support systems to ensure long-term success and well-being.