
What are the factors affecting BMI?
No one can stay fit and feel good without keeping a healthy weight. Indeed, today's advanced era is flooded with social media platforms providing a lot of information about weight and its related aspects. However, not everything is worthy of belief. Among the reliable parameters, Body mass index or BMI is the parameter that can give a general idea about your weight. It can provide you with information on whether you lie in a healthy weight range, overweight or obese. But there are numerous elements that can be influential on your BMI.
Understanding the various factors affecting BMI aids in developing a response to obesity or undernutrition and in gauging the overall metabolic health of individuals. A compassionate weight loss specialist like Dr Tahir Yunus at ALSA Pakistan can even help you with his knowledgeable opinion and expertise. The remainder of the article will address the biological, lifestyle, and environmental factors and economic determinants that construct BMI, specifically how these determinants impact an individual's weight status.
What is a BMI?
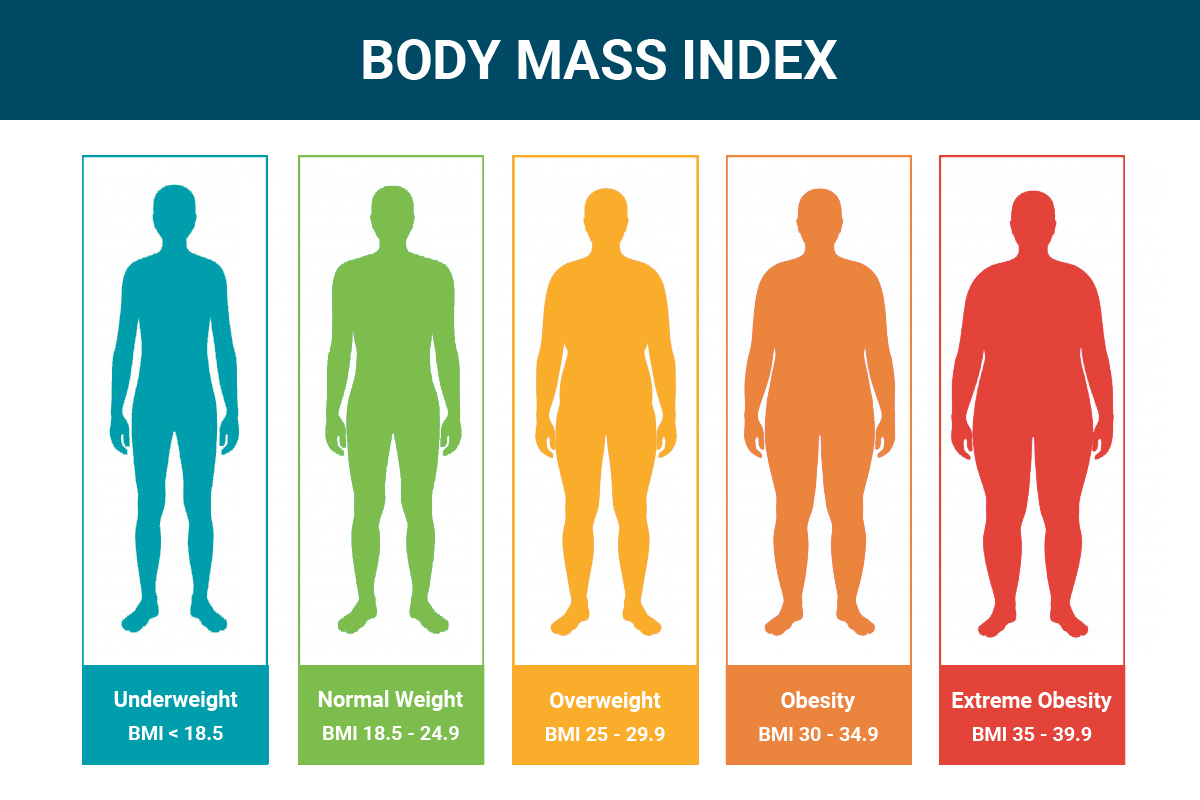
Body Mass Index (BMI) is commonly used as a metric for analysing an individual's body weight relative to height, measured in kilograms divided by the height squared in metres (kg/m²). BMI is a highly affordable, quick initial screening measure to categorize individuals as underweight, normal, overweight, and obese. It is useful for a population, though it does not differentiate fat and muscle mass or fat distribution.
However, it remains an essential element when completing evaluations in public health and clinical practice.
The general formula to calculate BMI is;
Weight in Kg /Height in m2
Further, according to the answer you get, you can know your weight status according to the following.
| BMI Range | Weight Category |
|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 - 24.9 | Normal weight |
| 25.0 - 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 - 34.9 | Obese (Class I) |
| 35.0 - 39.9 | Obese (Class II) |
| 40.0 or above | Obese (Class III) |
Elements That Significantly Impact Your BMI
Calculating BMI is an effective way to get first-hand information about an individual’s weight status. However, what can be influential in this regard is important to consider. Here are some significant elements one should not ignore.
1. Biological and Genetic Determinants
Among the biological determinants, the following are of immense significance;
Genetics
A notable factor regarding an individual's phenotype is how the body stores and expends energy. Generally, genetics is associated with an individual's body composition and metabolism. Studies indicate that genetics is generally accountable for 30–70% of the variance of an individual's BMI. Some genes are involved in appetite control, energy metabolism and the effectiveness of fat storage in the body. A person with a family history of obesity is at increased risk for being overweight; however, genetics alone does not account for BMI. It interacts with behaviour and the environment.
Age
Age is a primary indicator of increases in BMI over time, generally due to metabolic changes and body composition. From childhood and into adolescence, BMI typically has a slow increase as the body develops. In the adult stage, an individual typically has a decreasing metabolic rate due to a decrease in muscle mass. It leads to a relative increase in fatness. However, in the aging stage, the adult may continue to lose muscle, leading to further mobilisation of BMI and dysfunction. The important factor to keep in mind with aging and BMI lies in the muscle being denser than fat.
Comorbidities
A person with one or more medical conditions must keep in mind that their hormonal system and metabolism are not like those of a healthy individual. Certain health conditions can directly affect how the body regulates weight, metabolism and fat storage. Case in point, hyperthyroidism slows down metabolic function, thus BMI drops significantly. At the same time, diseases associated with insulin sensitivity can increase appetite and body composition. In this way, comorbidities not only coexist with variations in BMI but can also play a direct role in influencing it through biological mechanisms.
Weight Management Is No Longer A Trouble: Visit Dr Tahir At ALSA Pakistan For Considerable Control Over Weight
2. Lifestyle Aspects
Another critical aspect of your weight status is the way you live. Hence, your BMI cannot be neutral to your lifestyle. The noteworthy elements are here.
Diet
What we eat is one of the most important factors affecting our general health, and in extension, our physiques. Diet is a basic factor that affects BMI, because it is one of the elements determining the balance between energy intake and use. When calorie-dense, processed and “junk” foods are consumed in excess later in the day, it will slowly push BMI results towards overweight or obesity. On the contrary, nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins (think about low-fat Greek yogurt) and whole grains help maintain body weight. Plus, when we eat irregularly, too much or find ourselves mindlessly noshing, our metabolic rhythm can be off track. As a result, it makes weight easier to gain and harder to lose. Following a healthy and aware diet pattern not only nourishes the body but also ensures lasting health benefits.
Physical activity
Your physical work is a matter of great attention, not only in the discussion of weight status but also overall health grade. This is why, among factors affecting BMI, it comes high on the list. Aside from weight loss, regular exercise improves mood, increases vitality, and supports the body's natural metabolic processes. Basically, being active is a great strategy to maintain a healthy BMI and to boost general well-being.
3. Psychological Elements
All the lifestyle aspects of an individual revolve around their psychology. This is why this is one of the leading factors affecting BMI. Emotions, relationships, and mental health status determine your eating patterns and metabolism. Here is a brief overview of how;
Stress
Stress is among the leading psychological causes and correlates with changes in BMI. When faced with stress, the body releases cortisol, a hormone that can stimulate appetite and lead to fat accumulation, particularly in the abdomen. People often switch to comfort eating and want high-calorie foods in stressful situations. It all leads to weight gain. On the contrary, some lose their appetites when stress hits, leading to weight loss and a lower BMI. Therefore, chronic stress may lead to abnormal feeding behavior and metabolic disorders.
Personal and Social Bondings
The impact of personal and social bonds on lifestyle is evident. Supportive relationships, whether personal or social, help a person to stay happy and stress-free. Consequently, eating remains healthy, and individuals feel motivated to participate in physical activities. Peer influence of the social circle that values fitness is also notable. Hence, social interactions are significantly impactful on mental well-being and therefore are determinant for weight regulation.
Sleep Patterns
Sleep is among the overlooked factors, but it plays a critical role in achieving a healthy BMI. Sleeping less or inadequate relaxation upsets hormones. It includes leptin and ghrelin that control hunger and satiety. This can result in heightened hunger, leading to overeating and weight gain. Furthermore, inadequate sleep diminishes energy levels, discouraging exercise as well as reducing metabolism levels. Regular, reparative sleeping promotes balance of hormones, improved eating choices, as well as general stability of weight.
Wrapping Up
To sum up, in today’s appearance-conscious age, weight status is among the hot topics that people frequently discuss. The story begins with the question of whether a person is overweight or not. Here enters BMI is a high-impact parameter that can demonstrate the weight category of an individual as underweight, healthy or obese. However, there is another notable side. There are numerous factors affecting BMI that need individualized consideration. Some prominent ones are age, genetics, lifestyle choices and psychological determinants. Keeping all in mind, it becomes easy to find the flaws that are keeping you away from a healthy weight range.
After finding that a person lies in the overweight or obese category, the best strategy is to consult an experienced surgeon like Dr Tahir Yunus at ALSA Pakistan. He is well-regarded for his clinical judgments and expertise in providing individualized weight loss programs. Hence, enabling the population to shift to healthier habits and improve the quality of life.

